Table of Contents
If you are a healthcare provider navigating Medicare, you might already be aware of MIPS, an acronym most whispered during compliance meetings or tossed around by billing specialists.
If not, then this guide is for you!
“What is MIPS in Medical Billing?”
Acronym MIPS stands for the Merit-based Incentive Payment System — it isn’t just another piece of healthcare jargon—it can directly influence how much you earn from Medicare. Think of it as the government’s report card on how well you’re balancing cost, quality, and technology in patient care.
As a part of Medicare’s Quality Payment Program, MIPS focuses on shifting the reimbursement model from volume to care. Merit-based incentive payment system eliminates the idea of “More patients you see, the more you’ll get paid” and promotes:
- Smarter resource allocation
- Better-quality care
- Tech-enabled patient engagement
That’s why decision makers should focus on improving their practice’s MIPS performance score. Do it right, and you earn rewards. Underperform, and penalties can shrink your Medicare reimbursement.
In this blog, let’s dive into everything about merit-based incentive payment system, why it matters for your practice, and how the four performance categories shape your score.
What Does MIPS Stand for in Healthcare?
Let’s start with the basics: What is merit-based incentive payment system?
MIPS is short for the Merit-based Incentive Payment System; a program built into the MACRA framework—formally known as the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015. In simpler terms, MACRA repealed the old Sustainable Growth Rate formula and replaced it with more predictable, value-based pay structures. That’s where MACRA MIPS comes into play.
What is MACRA MIPS?
MACRA (Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015) transformed how Medicare pays providers, shifting from volume to value. It replaced the old Sustainable Growth Rate formula with a performance-based system rewarding quality, efficiency, and accountability in care.
At its core is MIPS (Merit-based Incentive Payment System), which adjusts Medicare Part B payments based on a provider’s performance across four key areas: Quality, Cost, Improvement Activities, and Promoting Interoperability.
Together, MACRA and MIPS drive a healthcare model that prioritizes better outcomes, smarter spending, and greater transparency.
What is the purpose of MIPS?
The Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) was created to connect Medicare reimbursements directly to provider performance—not just patient volume. Instead of being paid solely for visits, clinicians are rewarded for showing that they:
- Deliver high-quality care
- Keep costs under control
- Use technology effectively
- Drive measurable improvements in patient outcomes
Who participates in MIPS?
Not every provider is required to join. MIPS typically applies to physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, clinical nurse specialists, and certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs). Eligibility depends on CMS thresholds, such as Medicare Part B patient volumes and revenues.
How does MIPS reporting work?
Providers report annually, but there’s a catch: your performance in one year impacts your Medicare payment adjustments in future years. That’s why proactive planning and consistent performance tracking are essential.
Pro tip: Think of MIPS like a year-long exam, where the final grade doesn’t just impact your reputation, but also your paycheck.
Why MIPS Matters
MIPS compliance isn’t just about checking a regulatory box—it’s about protecting revenue, improving care, and future-proofing your practice. Here’s why it matters:
Financial Impact Is Immediate
Each year, CMS adjusts Medicare payments based on your MIPS score. High performers can earn positive adjustments (bonuses), while non-compliant providers face penalties of up to 9% of their Medicare reimbursements. That’s the difference between staying profitable and falling behind for many practices.
What is a good MIPS score?
Your MIPS score isn’t just a number—it’s money on the line.
👉 Score below 75, and your 2027 Medicare reimbursements could drop by -9%.
👉 Hit 75+, and you’re in the game for bonus payments (scaled to budget neutrality).
Better Scores = Competitive Advantage
MIPS scores are public on CMS’s Physician Compare website. Patients, payers, and referral partners increasingly look at these ratings. A strong score signals trust, quality, and reliability—helping your practice stand out.
Drives Care Quality & Efficiency
The program isn’t just paperwork. By tracking quality measures, interoperability, and practice improvement, MIPS forces practices to adopt workflows that reduce errors, improve patient communication, and streamline reporting. In the long run, it raises the standard of care.
Future-Ready Compliance
Healthcare regulations are tightening. Practices that build solid MIPS reporting processes now are better prepared for evolving value-based care models. Compliance today is risk-reduction tomorrow.
What are the 4 Categories of MIPS? Complete Overview
If MIPS is the exam, then these four categories are the questions. Together, they form your composite performance score, which dictates your payment adjustment. Here’s the breakdown:
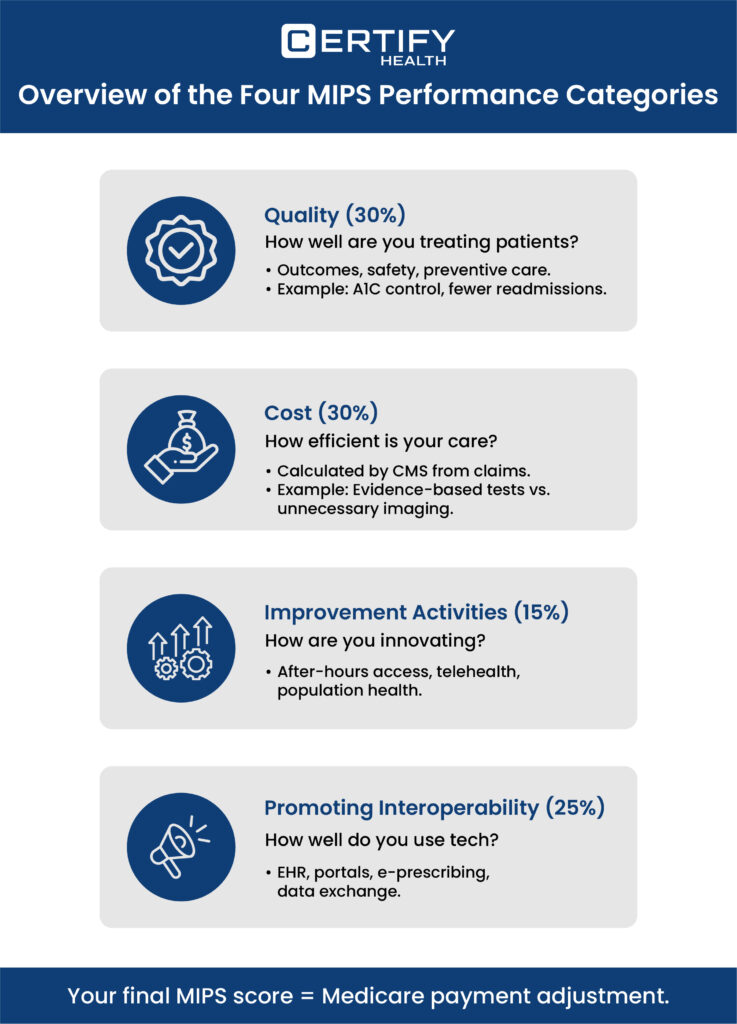
1. Quality (30% of Total Score)
This category asks a simple but heavy question: How well are you treating patients?
You’ll submit data on key measures that capture patient outcomes, safety, and effectiveness of care. For example:
- Are diabetic patients maintaining healthy A1C levels?
- Are hospital readmissions being reduced?
- Is patient preventive care documented?
From a practice perspective, the “Quality” bucket is where clinical excellence meets measurable proof. Because it’s weighted heavily, prioritizing quality reporting should be step one in your MIPS strategy.
2. Cost (30% of Total Score)
This category is all about efficiency. Unlike quality, you don’t have to submit cost data—CMS calculates it based on your Medicare claims.
Example in practice: Two providers treat patients with the same condition. One uses extensive, expensive imaging that doesn’t change treatment outcomes; the other uses conservative, evidence-based testing. The second provider scores higher in cost-efficiency.
For practices, this means smart resource utilization—delivering care that aligns with evidence while avoiding waste.
3. Improvement Activities (15% of Total Score)
Now here’s your chance to showcase practice innovation. Improvement Activities MIPS reward you for initiatives that enhance care delivery, coordination, and patient involvement.
Things like:
- Setting up after-hours patient communication channels
- Engaging in population health management
- Expanding telehealth capabilities
The beauty here is flexibility—practices choose improvement activities that align with size, specialty, and strategic goals. Think of it as your opportunity to get credit for doing things you should already be doing to thrive in modern healthcare.
4. Promoting Interoperability MIPS (25% of Total Score)
This is where technology plays its starring role. Promoting Interoperability MIPS focuses on how effectively you leverage certified EHR systems to share information, e-prescribe, and enable patient access to records. Ask yourself:
- Can patients log into portals?
- Can you transmit information across systems seamlessly?
- Can your practice prove you’re exchanging data for care coordination?
The takeaway: Better tech adoption = higher performance + more streamlined care delivery.
How These Categories Work Together
Every category adds weight to your overall MIPS score.
- Quality = 30%
- Cost = 30%
- Improvement Activities = 15%
- Promoting Interoperability = 25%
It’s a balanced equation, but with heavy emphasis on cost and quality. That means clinical decisions and financial stewardship weigh most heavily.
Your Medicare reimbursement shifts depending on how your score measures against CMS standards. The higher the score, the larger the upward adjustment.

How to Optimize Your MIPS Performance
Here’s where practices can turn strategy into action:
Stay Updated: CMS makes annual rule changes. Missing updates could mean missing out on bonus points.
Pick Smart Measures: Instead of spreading thin, focus on measures aligned with your clinical strengths and patient mix.
Monitor Year-Round: Don’t wait until submission season. Review your data regularly and track performance on dashboards.
Submit Smoothly: For reliable data, lean on certified EHRs—registries offer an added layer of seamless submission support.
Team Involvement: Training staff ensures front-office, nursing, and physician teams understand their role in data capture and compliance.
Leverage Easy Wins: Choose improvement activities in MIPS that yield high credit with low administrative burden—like patient communication tools or chronic disease management workflows.
Stay Clinically Grounded: Don’t chase points at the expense of care. Align MIPS strategy with what’s right for your patients.
Conclusion
The Merit-based Incentive Payment System represents a pivotal shift in how Medicare rewards care. It’s not just about seeing patients—it’s about delivering care that checks boxes on quality, cost, improvement, and interoperability.
For decision-makers, understanding MIPS eligibility, capturing the right data, and optimizing performance can safeguard against penalties while creating opportunities for higher reimbursements.
In short: MIPS isn’t going away. It’s a reality designed to drive value-based care forward. Practices that embrace its framework will not only fare better financially but also set themselves apart in a marketplace demanding transparency and measurable quality.
So, what’s your next move? Start by asking yourself: How ready is my practice to maximize performance across MIPS categories?
The better you answer that internally, the stronger your external outcomes—both for patients and for your bottom line.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is MIPS payment calculated?
Here’s how your MIPS score is calculated:
The sum of the weighted score for each of the four performance categories– quality (30%), promoting interoperability (25%), improvement activities (15%), & Cost (30%)+ the bonus points earned determines your MIPS score.
MIPS Final Score=(Q×0.30)+(PI×0.25)+(IA×0.15)+(C×0.30)+Bonus Points
What is Medicare Part B?
Medicare Part B is a component of Medicare medical insurance that covers necessary medical services, including medical supplies, outpatient care, therapy, ambulance services, and preventive care services.
It covers doctor’s visits, durable medical equipment, and ambulance services. Patients pay a monthly premium, a deductible, & 20% co-pay to use Medicare Part B.
What Medicare Part B does not cover: routine dental, hearing, or vision care, long-term care, routine prescription drugs, and cosmetic surgery.
What is MIPS eligibility?
Clinicians qualify for MIPS if they exceed all three low-volume thresholds: over $90,000 in Medicare Part B charges, 200+ patients, and 200+ services. Eligible types include physicians, PAs, NPs, and PTs. Those below the threshold are exempt but may participate voluntarily.
How does a merit-based incentive payment system work?
MIPS works by rewarding providers for the quality and value of care they deliver, not just the number of patients they see.
It evaluates performance across four key categories: Quality, Cost, Improvement Activities, and Promoting Interoperability.
Each category contributes to a composite MIPS score, which determines whether a provider earns a positive, neutral, or negative payment adjustment to their Medicare reimbursement.
In short, higher performance means higher incentives and stronger care accountability.