Table of Contents
MRI delays in orthopedic workflows are not incidental or occasional. They are systemic, well-documented, and measurable.
Delays in MRI completion, prior authorization processing, and surgical readiness have direct effects on clinical care, operational efficiency, and patient outcomes.
This blog breaks down exactly where the workflows fail, why most “automation advice” on the internet is ineffective, and which specific automation interventions have the suitable fixes.
The Problem: MRI Delays and Prior Authorization Burden Are Real, Systemic, and Quantified
Dermatology combines high visit volume with high documentation and billing complexity. That combination is rare and unforgiving when workflows are manual.
MRI Wait Times Are Long Enough to Impact Orthopedic Care
According to current U.S. national data:
- Routine MRI waits often range from 2 to 4+ weeks, even when the scan itself takes 15 minutes.
- Nearly 50% of outpatient MRI orders are delayed more than 10 days beyond the originally scheduled date.
- MRI results often take 1 to 2 weeks for radiology interpretation due to staffing bottlenecks in reporting.
These delays are large compared with the clinical windows in orthopedic decision making. Surgery planning often depends on MRI findings within a narrow timeframe.
Prior Authorization Delays and Administrative Burden Are Measurable and Painful
Orthopedic practices in the U.S. face major bottlenecks with prior authorization:
- An averaged prospective multicenter analysis found that only 1.5% of advanced imaging or surgical prior authorizations were denied, but that the overall process still caused significant delays in care because nearly all required review.
- On average, staff spent 19.5 minutes per authorization request processing documentation.
- Patients waited 2.2 days on average for initial authorization output, but about one-third of appeals remained unresolved 30 days or more after submission.
- Although 96.5% of requests were ultimately approved, the delay remained a substantial barrier to access.
Physician Experience with Prior Authorization Confirms Patient Harm and Delay
The American Medical Association’s latest national survey of 1,000 U.S. physicians found:
- 93% reported that prior authorization delayed patient care.
- 83% said prior authorization led patients to abandon treatment.
- 29% reported that prior authorization delays had resulted in a serious adverse event (e.g., hospitalization, disability, or death).
- 40% reported employing staff whose only job was prior authorization work.
This is not about denial rates. It is about time, harm, and system cost.
MRI Performance Delays Are Not Only Authorization-Related
A comprehensive analysis of outpatient MRI orders at a major radiology system found:
- Of 97,160 unique MRI orders with expected same-day or 1-day performance, 48% were delayed more than 10 days from the ordering provider’s intended date.
- Mean time from order placement to performance was 18.5 days.
These delays are not trivial. For orthopedic cases, a 10-plus day deviation from the intended imaging date routinely disrupts surgical schedules and care plans.
Why Most Automation Advice Is Shallow and Ineffective
The common narrative in orthopedic operations blogs is:
- “Adopt PACS and EHR automation and imaging delays will go down.”
- “Integrate imaging with scheduling.”
- “Better documentation improves throughput.”
These points are true as far as they go. But they do not address the real bottlenecks:
- Prior authorization response time logic
- Imaging order completeness and accuracy
- Validity windows relative to surgical planning
- Inefficient cross-team communication
- Lack of measurement of pre-surgical readiness metrics
All of these are measurable data flows; they are where delays originate, not in scanner speed or storage.
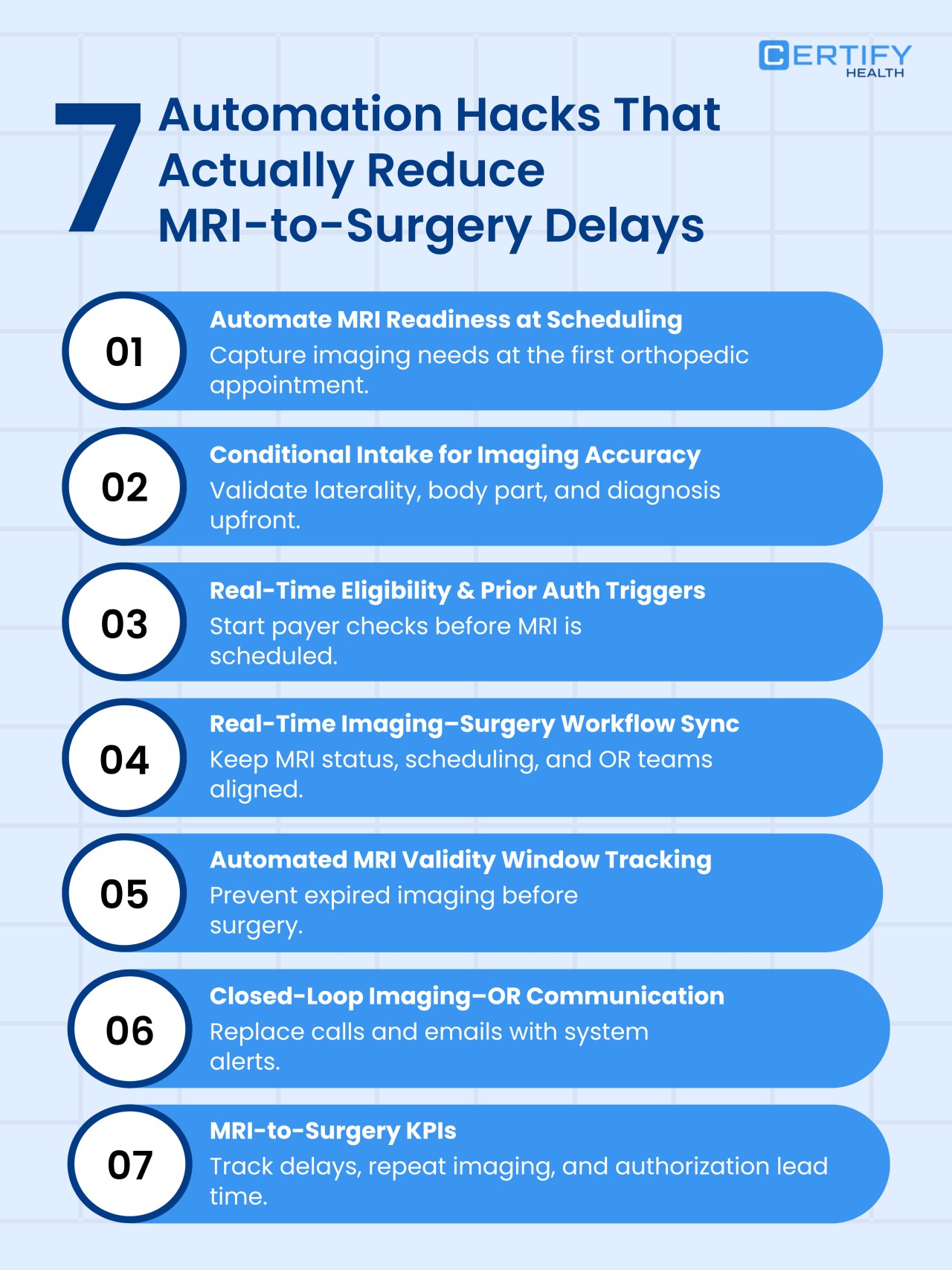
7 Automation Hacks to Speed Up MRI-to-Surgery Timelines in Orthopedic Workflows
Here are the interventions that solve measured causes of delay, along with data showing why each intervention is critical.
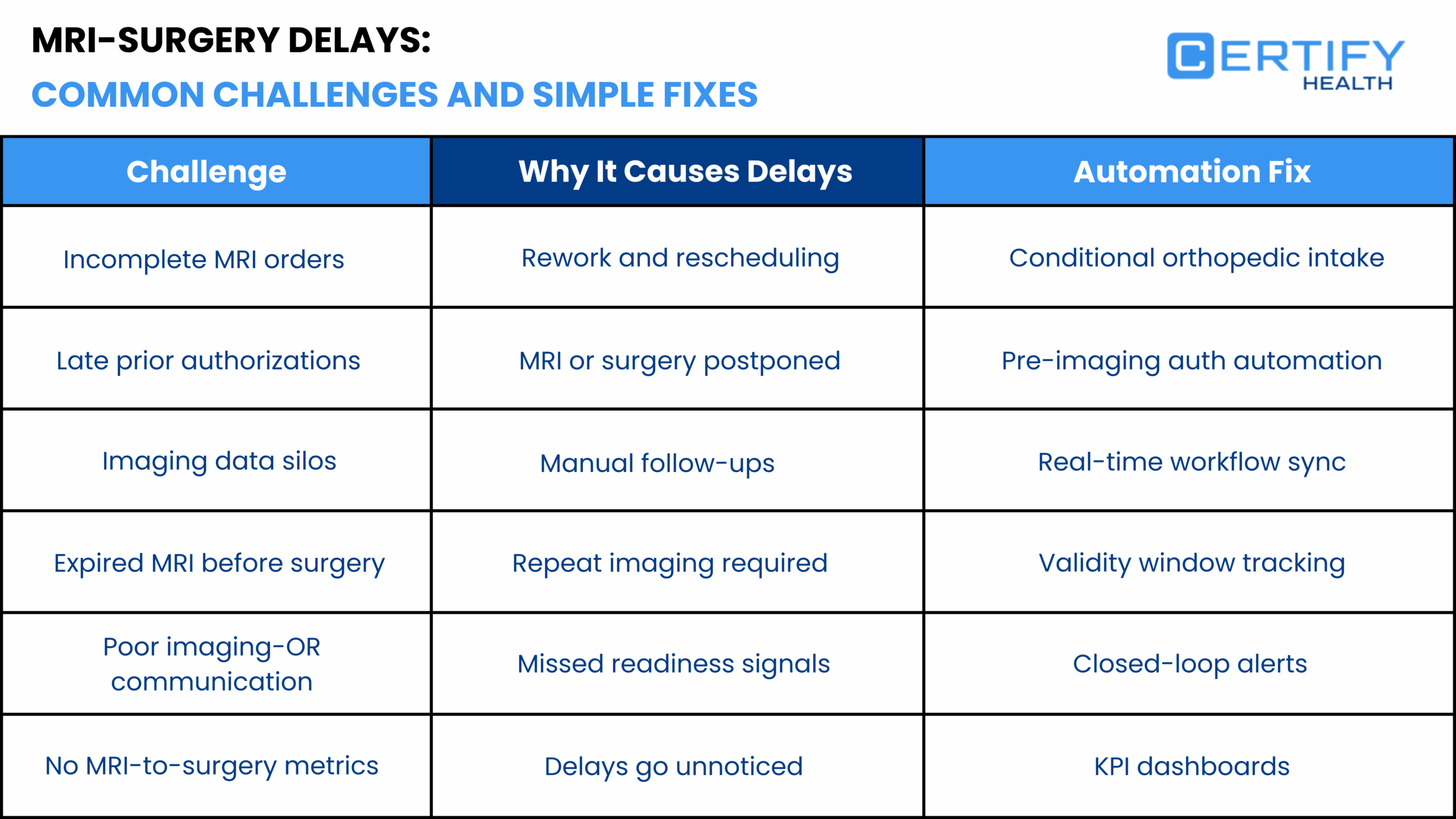
1. Enforce Complete Clinical Orders at the Time of MRI Scheduling
What Breaks
Incomplete orders are repeatedly found to delay authorization. These include the ones missing laterality, symptom detail, conservative treatment history, or precise diagnosis.
Such gaps force payers to request more documentation, delaying approval and execution.
CMS defines advanced imaging medical necessity documentation that includes symptom duration, failed conservative therapy, and relevant clinical context.
Evidence
Orders missing key clinical elements have been shown to increase authorization time significantly. One study found incomplete orders were associated with up to ~2.5× slower processing times.
What the Automation Must Do
- Validate required clinical fields before order submission
- Prevent imaging scheduling until those fields are complete
- Provide real-time prompts tied to CMS medical necessity rules
Impact
This intervention eliminates the most common cause of backend rework and rescheduling. Without it, all downstream automation fails.
2. Validate Laterality and Anatomy Using Conditional Intake Logic
What Breaks
Laterality errors are a documented issue in MRI and other musculoskeletal imaging workflows. Peer-reviewed radiology quality studies report laterality discrepancies in approximately 0.2–1.5% of imaging reports, errors that typically require clarification, correction, or repeat submission. This creates avoidable delays into downstream authorization and scheduling processes.
CMS billing compliance rules require laterality to match the clinical diagnosis and the imaging order.
What the Automation Must Do
- Require matched laterality, body part, and diagnostic alignment at the time of entry
- Block entry until validated
- Provide immediate feedback that eliminates ambiguity
Impact
Reducing order errors reduces repeat imaging, wasted radiology capacity, and denial risk.
3. Trigger Prior Authorization in Real Time Immediately After Order Validation
What Breaks
Delayed prior authorization submission is the most measurable single cause of MRI delivery delay.
AMA survey data shows that 93% of physicians report delays in care due to prior authorization.
Other research shows that while denial rates may be low, the time to authorization is prolonged, often taking multiple days or weeks because submission is done after scheduling, not before.
What the Automation Must Do
- Immediately send authorization package as soon as the order is validated for completeness
- Use structured clinical data to prevent manual assembly of authorization documents
- Track authorization status in real time
Impact
Earlier payer responses reduce reschedules, cancellations, and patient dissatisfaction.
4. Track Authorization Lead Time as a Surgical Risk KPI
What Breaks
Most practices do not treat authorization lead time as a key operational metric.
A multicenter study found that even when approval rates were high, appeals could remain unresolved beyond 30 days, delaying care significantly.
AMA surveys show that 40% of physician practices allocate dedicated staff exclusively to prior authorization work because it is so time consuming.
What the Automation Must Do
- Measure the time from order submission to authorization decision
- Flag cases exceeding acceptable thresholds (e.g., >7 days)
- Trigger escalations or targeted intervention
Impact
This turns authorization time from a hidden cost into a visible metric that can be reduced.
5. Actively Manage Imaging Validity Windows Relative to Surgical Dates
What Breaks
Imaging findings become less relevant as time passes. Peer reviewed research shows that imaging changes over weeks can alter clinical management.
CMS prohibits paying for tests that are not medically necessary at the time of service.
What the Automation Must Do
- Track the age of imaging relative to the scheduled surgery
- Re-validate imaging before OR scheduling
- Alert care teams before validity expires
Impact
This prevents last minute repeat MRI and unnecessary claim denials due to outdated imaging.
6. Create Closed Loop Imaging and Surgery Communication Channels
What Breaks
WHO diagnostic safety frameworks identify lack of closed loop communication as a key factor in delays and errors.
AMA surveys show that poor communication across clinical teams is routinely cited as a cause of delayed care.
What the Automation Must Do
- Provide real-time status updates to surgeons, schedulers, and imaging centers
- Automate task assignment when imaging results change
- Create a shared dashboard of readiness indicators
Impact
Visibility eliminates guesswork and prevents unnecessary repeat imaging orders.
7. Track MRI-to-Surgery Interval and Repeat Imaging as Operational KPIs
What Breaks
Studies show that nearly half of MRI orders are delayed more than 10 days from when the ordering provider expected them. But most practices do not measure this.
What the Automation Must Do
- Track MRI order date to completion date intervals
- Record repeat imaging rates
- Correlate intervals with surgery delay and patient outcomes
Impact
This anchors the entire workflow in evidence and enables continuous improvement.
Evidence-Based Operational Summary
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Outpatient MRI orders delayed >10 days | ~48% |
| Average MRI wait time (U.S.) | 2–4+ weeks |
| AMA Physicians reporting prior authorization delays | 93% |
| MRI prior authorization denial rate | ~4.94% |
| Average administrative time per authorization | 19.5 minutes |
| Appeals unresolved >30 days | ~33% |
| Physician practices using dedicated PA staff | ~40% |
How CERTIFY Health Orchestrates MRI-to-Surgery Readiness Across Orthopedic Workflows
Most orthopedic technology stacks were built to optimize individual steps. An EHR for documentation. A PACS for imaging storage. A scheduling system for appointments. A clearinghouse for eligibility. Each tool performs its function, but none owns readiness across the MRI-to-surgery continuum.
This gap is precisely where delays, repeat imaging, and lost surgical throughput originate.
CERTIFY Health is not positioned as another point solution. It functions as an orchestration layer that enforces sequencing, validates readiness, and synchronizes imaging, authorization, and surgical workflows in real time.
From Fragmented Tasks to Enforced Readiness States
Federal research consistently shows that diagnostic and procedural delays arise when prerequisites are incomplete or invisible at the time downstream actions are taken. CMS quality guidance emphasizes the importance of sequencing and pre-service validation to reduce postponed procedures and wasted capacity.
CERTIFY Health operationalizes this principle by converting orthopedic workflows into explicit readiness states:
- MRI orders cannot progress unless required clinical elements for medical necessity are complete
- Prior authorization is triggered automatically once clinical readiness is achieved, not days later
- Imaging completion, authorization status, and validity windows are continuously evaluated against scheduled surgery dates
- Operating room scheduling is gated by verified diagnostic readiness rather than assumptions or manual checks
This design directly addresses a reality highlighted in U.S. research. While denial rates for imaging may be under five percent, the time cost of rework and delay remains high. CERTIFY Health reduces that time cost by preventing incomplete or premature handoffs.
One System of Record for Imaging and Surgical Readiness
A core contributor to repeat MRI and delayed surgery is lack of trust. Surgeons repeat imaging when they are unsure whether prior scans are current, authorized, or accessible. Research identifies uncertainty about imaging validity and accessibility as a non-clinical driver of repeat diagnostics.
CERTIFY Health resolves this by providing a single authoritative readiness view that includes:
- Imaging completion status across internal and external imaging centers
- Authorization state with payer response timelines
- Imaging age relative to payer rules and clinical protocols
- Flags for expiration risk before scheduled surgery
This replaces manual reconciliation, phone calls, and spreadsheet tracking with real-time system logic. When surgeons and schedulers share the same readiness signal, defensive repeat imaging declines.
Built for the Reality of Orthopedic and Imaging Ecosystems
Orthopedic practices rarely control their entire imaging footprint. Imaging may occur at hospital outpatient departments, independent imaging centers, or partner facilities using different PACS and EHR systems.
CERTIFY Health is designed to be EHR-agnostic and imaging-agnostic, allowing orthopedic groups to coordinate MRI readiness across multiple sites without forcing consolidation or replacement of existing systems.
This matters because CMS and WHO diagnostic safety guidance both identify information discontinuity across organizations as a major contributor to diagnostic delay. CERTIFY Health addresses this risk by centralizing workflow logic without centralizing clinical systems.

What Changes Operationally After Adoption
When orthopedic practices implement CERTIFY Health as the workflow orchestration layer, three operational shifts occur:
- MRI delays are identified days earlier rather than discovered at the point of surgical scheduling
- Authorization lead time becomes a managed variable rather than an unpredictable bottleneck
- Repeat imaging transitions from a reactive safety behavior to a measurable exception
These are not cosmetic improvements. They directly align with CMS and AMA findings that delays in prior authorization and diagnostic readiness drive postponed care, patient attrition, and staff burnout.
CERTIFY Health does not promise faster scanners or fewer payer rules. It ensures that every downstream action occurs only when upstream readiness is verified.
That is the difference between automation that digitizes tasks and automation that actually reduces MRI-to-surgery delay.
Final Takeaway
MRI to surgery delays in orthopedic practices are not random. They are measured, structural failures in workflow design, governance, and readiness sequencing.
The numeric evidence above shows that:
- MRI scheduling delays affect nearly half of orders
- Prior authorization delays impact most practices
- Authorization processes often take weeks before meaningfully moving care forward
- Repeat imaging is often a symptom of coordination failure
Automation only works when it enforces complete orders, validates ready states, tracks time-based risk, and connects teams in real time.
Anything else is digital paperwork.























